NASA Glenn Studies Pot-ability of Litz Wires with Robo-Met
November 14, 2019
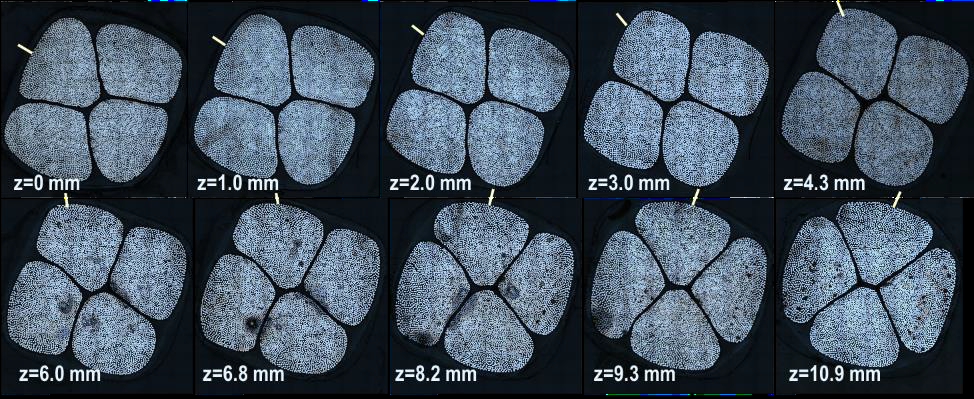 Robo-Met has a long history of providing 3D insights to materials science research, but NASA Glenn Research Center leveraged their serial sectioning system for a new and unique application. Dr. Euy-Sik Eugene Shin and the teams at NASA Glenn recently published their work on using the Robo-Met.3D® automated metallography system to develop a detailed 3D model of the structure (wire twist, bundle packing, and shape) of Litz wires.
Robo-Met has a long history of providing 3D insights to materials science research, but NASA Glenn Research Center leveraged their serial sectioning system for a new and unique application. Dr. Euy-Sik Eugene Shin and the teams at NASA Glenn recently published their work on using the Robo-Met.3D® automated metallography system to develop a detailed 3D model of the structure (wire twist, bundle packing, and shape) of Litz wires.
Read also: NASA Glenn Acquires Robo-Met.3D Unit from UES to Expand Materials Characterization Capabilities
Litz wires are used in NASA Glenn’s High Efficiency Megawatt Motor (HEMM). The effects of the non-uniformity on overall power density of conductor windings and heat dissipation optimization will be systematically examined as part of this work.
Robo-Met.3D results were compared to micro-CT results from an X-Ray WorX SE-225 (160 kV, 100 µA) microfocus x-ray source with Dexela 2923 detector. The authors concluded that “microCT might not be a good option since extremely high power was required for penetration..." Even with increased focal spot size, significant scatter was present at the interior regions. "On the other hand, the serial polishing coupled with high resolution microscopy provided sequences of high resolution cross-sectional images..."
Read the full article, published in the AIAA Propulsion and Energy 2019 Forum, here: Pot-ability Assessment of Litz Wires for High Power Density Electric Motor."
Read also: Robo-Met Publications in 2019
Questions? Contact us here. Connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Instagram to stay in the loop!
